Detect Contours
SUMMARY
Detect Contours detects object outlines using a contour-based detector.
Contour detection extracts continuous boundary curves from edges in an image to describe object shape. It works best when object boundaries are clear and contrast well with the background.
Use this Skill when you want to extract object contours for shape analysis.
The Skill
from telekinesis import retina
annotations = retina.detect_contours(
image=image,
retrieval_mode="retrieve_list",
approx_method="chain_approximate_simple",
min_area=200,
max_area=100000,
)Example
Input
Original binary image
Detected Contours and Bounding Box
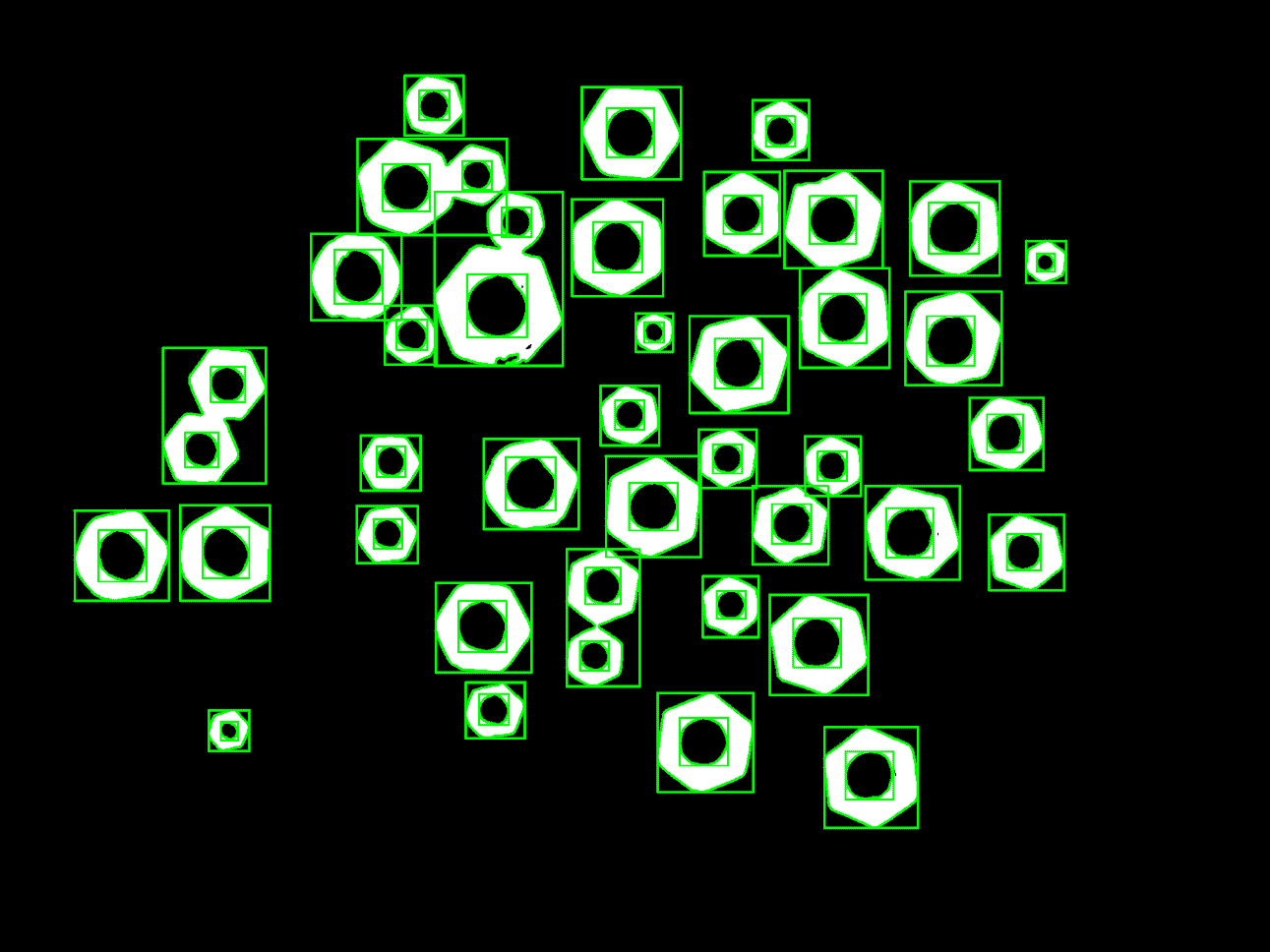
Image overlaid with detected contours and bounding boxes.
The Code
from telekinesis import retina
from datatypes import io
import pathlib
# Optional for logging
from loguru import logger
DATA_DIR = pathlib.Path("path/to/telekinesis-data")
# Load image
filepath = str(DATA_DIR / "images" / "nuts_scattered_filtered_gaussian.png")
image = io.load_image(filepath=filepath, as_binary=True)
logger.success(f"Loaded image from {filepath}")
# Detect circles
annotations = retina.detect_contours(
image=image,
retrieval_mode="retrieve_list",
approx_method="chain_approximate_simple",
min_area=200,
max_area=100000,
)
# Access results
annotations = annotations.to_list()
logger.debug(f"Detected {len(annotations)} contours using contour detector.")The Explanation of the Code
This example shows how to use the detect_contours Skill to extract object outlines from a binary image. The code begins by importing the necessary modules from Telekinesis and Python, and optionally sets up logging with loguru to provide feedback during execution.
from telekinesis import retina
from datatypes import io
import pathlib
# Optional for logging
from loguru import loggerThe image is loaded from a .png file using io.load_image. The logger immediately reports the path of the image loaded, helping confirm the input is correct and ready for processing.
DATA_DIR = pathlib.Path("path/to/telekinesis-data")
# Load image
filepath = str(DATA_DIR / "images" / "nuts_scattered_filtered_gaussian.png")
image = io.load_image(filepath=filepath, as_gray=True)
logger.success(f"Loaded image from {filepath}")The detection parameters are configured:
imagespecifies the input binary imageretrieval_modecontrols which contours are returned (for example, a full list vs. hierarchical retrieval)approx_methodcontrols the contour approximation strategy to simplify boundary pointsmin_areasets the minimum contour area to keepmax_areasets the maximum contour area to keep
annotations = retina.detect_contours(
image=image,
retrieval_mode="retrieve_list",
approx_method="chain_approximate_simple",
min_area=200,
max_area=100000,
)The function returns an annotations object in COCO-like format. Extract the detected contours as follows. The logger outputs the number of contours detected.
# Access results
annotations = annotations.to_list()
logger.debug(f"Detected {len(annotations)} contours using contour detector.")This workflow focuses on the Skill itself: it provides a fast, parameter-driven approach to contour detection, useful for extracting object boundaries and performing downstream measurements such as area, perimeter, and shape analysis in industrial vision pipelines.
Running the Example
Runnable examples are available in the Telekinesis examples repository. Follow the README in that repository to set up the environment. Once set up, you can run this specific example with:
cd telekinesis-examples
python examples/retina_examples.py --example detect_contoursHow to Tune the Parameters
The detect_contours Skill has several tunable parameters. Key ones:
retrieval_mode:
- Controls which contours are returned (for example, all contours vs. hierarchical retrieval)
- Typical choices:
retrieve_list,retrieve_tree - Use
retrieve_listfor a flat list; use a hierarchical mode when parent/child contour relationships matter
approx_method:
- Controls the contour approximation strategy used to simplify boundary points
- Typical choices:
chain_approximate_simple,chain_approximate_none - Use
chain_approximate_simpleto reduce points and speed up downstream processing
min_area:
- Minimum contour area to keep
- Units: Pixels squared
- Increase to filter out small noise blobs
- Typical range: depends on image resolution and object size
max_area:
- Maximum contour area to keep
- Units: Pixels squared
- Decrease to remove large background regions or merged contours
- Typical range: depends on image resolution and object size
TIP
Best practice: Start with min_area tuned to remove noise, keep max_area high, and use chain_approximate_simple for faster processing. Switch retrieval modes only when you need hierarchy.
Where to Use the Skill in a Pipeline
Detect Contours is commonly used in the following pipelines:
- Object shape analysis – Extracting outlines for shape descriptors and measurements
- Quality inspection – Checking part boundaries, defects, and edge consistency
A typical pipeline for object contour extraction looks as follows:
from telekinesis import retina
from datatypes import io
# 1. Load the image (as binary)
image = io.load_image(filepath=..., as_binary=True)
# 2. Apply Gaussian blur to reduce noise.
smoothed = pupil.filter_image_using_gaussian_blur(image=image, ...)
# 2. Detect contours
annotations = retina.detect_contours(
image=smoothed,
retrieval_mode="retrieve_list",
approx_method="chain_approximate_simple",
min_area=10,
max_area=100,
)
# 3. Extract contour annotations
annotations = annotations.to_list()
# 4. Optionally extract contour points
contours = []
for annotation in annotations:
contour_points = annotation["geometry"]["points"]
contours.append(contour_points)Related skills to build such a pipeline:
filter_image_using_gaussian_blur: More sophisticated smoothing with better quality
Alternative Skills
| Skill | vs. Detect Contours |
|---|
When Not to Use the Skill
Do not use Detect Contours when:
- Object boundaries are weak or low-contrast (contours will be fragmented or missing)
- Images are heavily textured or noisy (can produce many false contours)
- Objects overlap significantly (contours may merge and lose individual shapes)
- You need sub-pixel boundary precision (contours are returned at pixel resolution)
TIP
Contour detection works best on clean, high-contrast edges. Apply preprocessing (e.g., denoising or thresholding) to improve boundary quality before detection.

