Filter Segments By Area
SUMMARY
Filter Segments By Area filters superpixels based on area.
Filter Segments By Area removes superpixels that are too small or too large based on area thresholds. This is useful for removing noise segments and keeping only objects of interest.
Use this Skill when you want to filter superpixels by area to remove noise or unwanted segments.
The Skill
from telekinesis import cornea
result = cornea.filter_segments_by_area(
image=image,
labels=labels,
min_area=10000,
max_area=100000,
)Example
Input Image
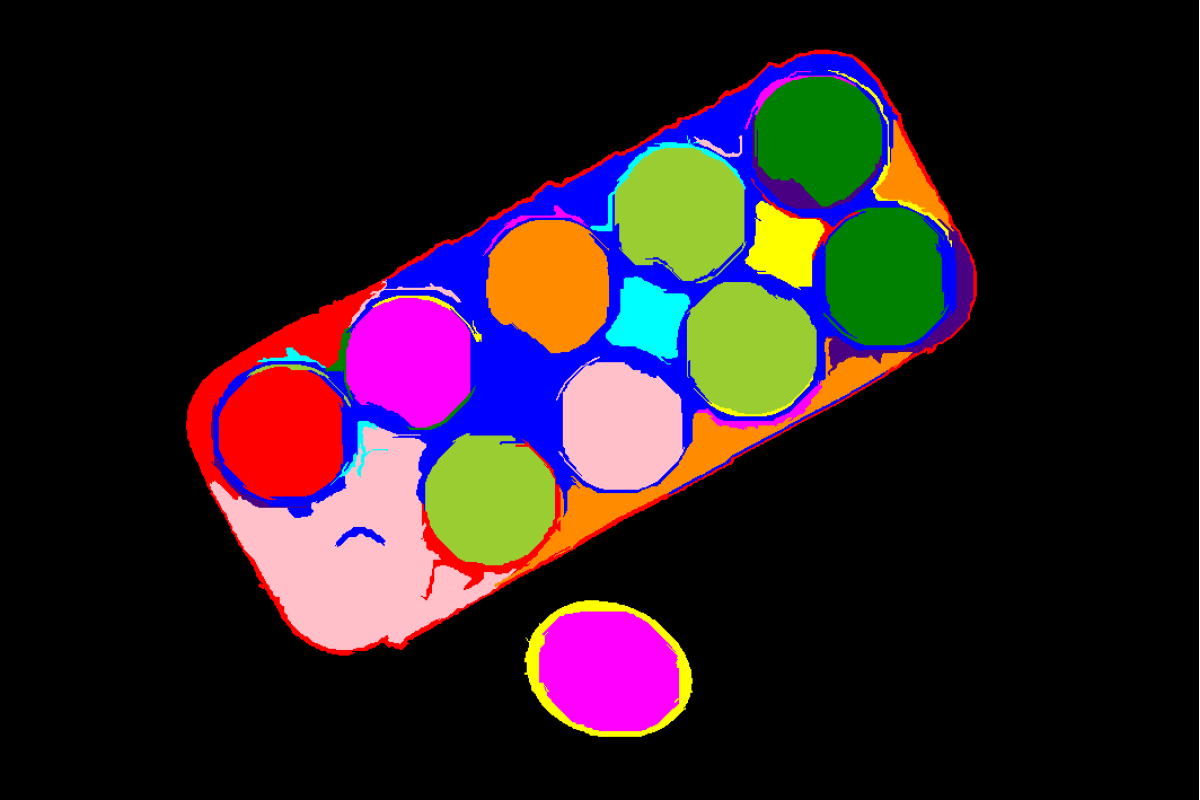
Original image with superpixels
Output Image
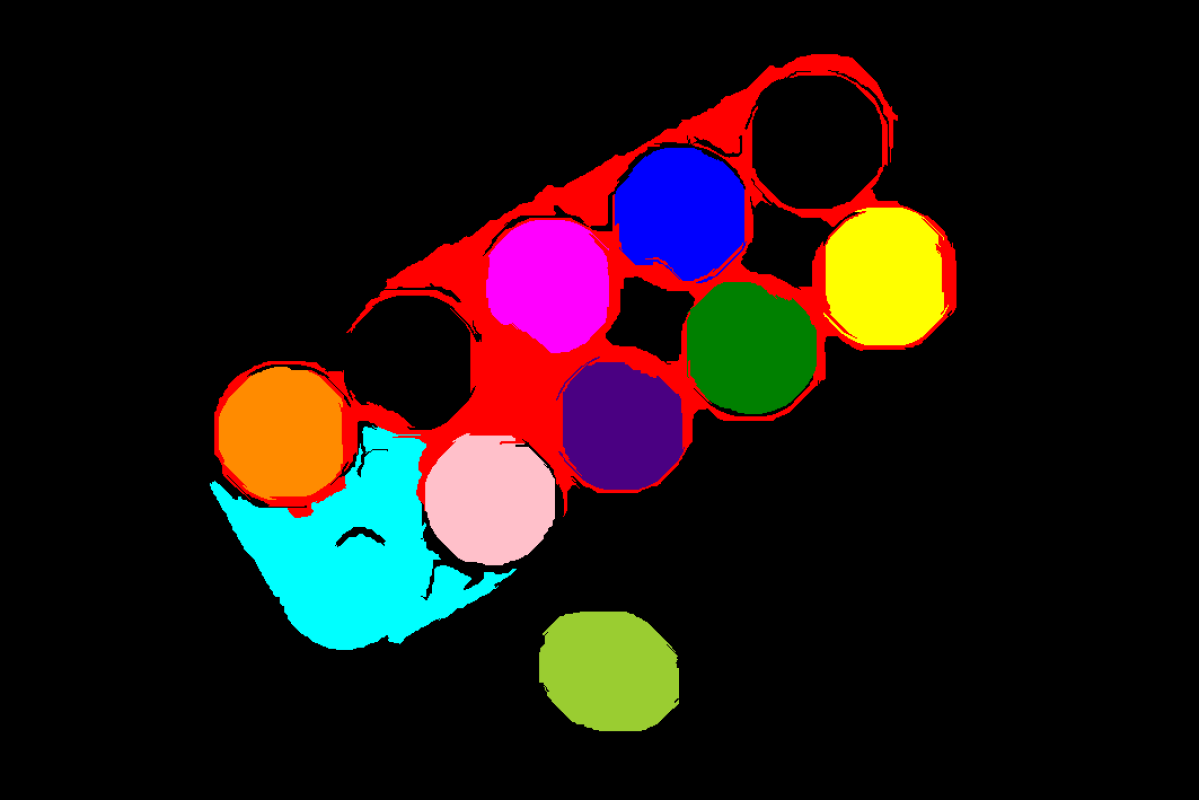
Filtered image - only segments within area range shown
The Code
import pathlib
from telekinesis import cornea
from datatypes import datatypes, io
DATA_DIR = pathlib.Path("path/to/telekinesis-data")
# Load image
filepath = str(DATA_DIR / "images" / "eggs_carton.jpg")
image = io.load_image(filepath=filepath)
# First, generate superpixels using Felzenszwalb
result_felzenszwalb = cornea.segment_image_using_felzenszwalb(
image=image,
scale=500,
sigma=1,
min_size=200,
)
# Extract superpixel labels
superpixel_labels = result_felzenszwalb["annotation"].to_dict()['labeled_mask']
superpixel_labels = datatypes.Image(superpixel_labels)
# Filter superpixels based on area
result = cornea.filter_segments_by_area(
image=image,
labels=superpixel_labels,
min_area=10000,
max_area=100000,
)
# Access results
annotation = result["annotation"].to_dict()
mask = annotation['labeled_mask']The Explanation of the Code
Filter Segments By Area removes superpixels that fall outside the specified area range, keeping only segments within min_area and max_area.
The code begins by importing the required modules, loading an image, and generating superpixels:
import pathlib
from telekinesis import cornea
from datatypes import datatypes, io
DATA_DIR = pathlib.Path("path/to/telekinesis-data")
filepath = str(DATA_DIR / "images" / "eggs_carton.jpg")
image = io.load_image(filepath=filepath)
# Generate superpixels first
result_felzenszwalb = cornea.segment_image_using_felzenszwalb(
image=image,
scale=500,
sigma=1,
min_size=200,
)
superpixel_labels = result_felzenszwalb["annotation"].to_dict()['labeled_mask']
superpixel_labels = datatypes.Image(superpixel_labels)The filter parameters are configured:
labelsis the label image from superpixel segmentationmin_areaandmax_areadefine the area range for keeping segments
result = cornea.filter_segments_by_area(
image=image,
labels=superpixel_labels,
min_area=10000,
max_area=100000,
)The function returns a dictionary containing an annotation object. Extract the mask as follows:
annotation = result["annotation"].to_dict()
mask = annotation['labeled_mask']Running the Example
Runnable examples are available in the Telekinesis examples repository. Follow the README in that repository to set up the environment. Once set up, you can run this specific example with:
cd telekinesis-examples
python examples/cornea_examples.py --example filter_segments_by_areaHow to Tune the Parameters
The filter_segments_by_area Skill has 3 parameters:
labels (required):
- Label image from superpixel segmentation
- Units: Image object
- Each unique value represents a different superpixel
min_area (default: 20):
- Minimum area for keeping segments
- Units: Pixels
- Decrease to keep smaller segments
- Increase to remove smaller segments (noise)
- Typical range: 10-100
max_area (default: 1000):
- Maximum area for keeping segments
- Units: Pixels
- Increase to keep larger segments
- Decrease to remove larger segments
- Typical range: 100-10000
TIP
Best practice: Use histogram analysis of superpixel areas to determine appropriate min_area and max_area values. Set min_area to remove noise, max_area to remove background regions.
Where to Use the Skill in a Pipeline
Filter Segments By Area is commonly used in the following pipelines:
- Noise removal - Remove small noise segments
- Object filtering - Keep only objects of specific sizes
- Post-processing - Refine superpixel segmentation
- Quality control - Filter defects by size
A typical pipeline for superpixel filtering looks as follows:
from telekinesis import cornea
from datatypes import datatypes, io
# 1. Load the image
image = io.load_image(filepath=...)
# 2. Generate superpixels
superpixel_result = cornea.segment_image_using_felzenszwalb(image=image, ...)
# 3. Extract labels
superpixel_labels = superpixel_result["annotation"].to_dict()['labeled_mask']
superpixel_labels = datatypes.Image(superpixel_labels)
# 4. Filter by area
result = cornea.filter_segments_by_area(
image=image,
labels=superpixel_labels,
min_area=10000,
max_area=100000,
)
# 5. Extract filtered mask
annotation = result["annotation"].to_dict()
mask = annotation['labeled_mask']Related skills to build such a pipeline:
segment_image_using_slic_superpixel: Generate superpixelssegment_image_using_felzenszwalb: Alternative superpixel methodfilter_segments_by_color: Filter by color instead of area
Alternative Skills
| Skill | vs. Filter Segments By Area |
|---|---|
| filter_segments_by_color | Filter by color instead of area. Use area for size-based filtering, color for color-based filtering. |
| filter_segments_by_mask | Filter using a mask. Use mask for spatial filtering, area for size-based filtering. |
When Not to Use the Skill
Do not use Filter Segments By Area when:
- You need to keep all segments (Don't filter)
- You need color-based filtering (Use filter_segments_by_color instead)
- You need spatial filtering (Use filter_segments_by_mask instead)
TIP
Filter Segments By Area is an essential post-processing step for superpixel-based pipelines to remove noise and unwanted segments.

