Segment Image Using SLIC Superpixel
SUMMARY
Segment Image Using SLIC Superpixel performs SLIC (Simple Linear Iterative Clustering) superpixel segmentation.
SLIC creates compact, nearly uniform superpixels by clustering pixels in a combined color and spatial space. It produces regular, grid-like superpixels that are efficient to compute and useful for many computer vision tasks.
Use this Skill when you want to create regular, compact superpixels using the SLIC algorithm.
The Skill
from telekinesis import cornea
result = cornea.segment_image_using_slic_superpixel(
image=image,
num_segments=2,
compactness=15.0,
max_iterations=20,
enforce_connectivity=True,
)Example
Input Image
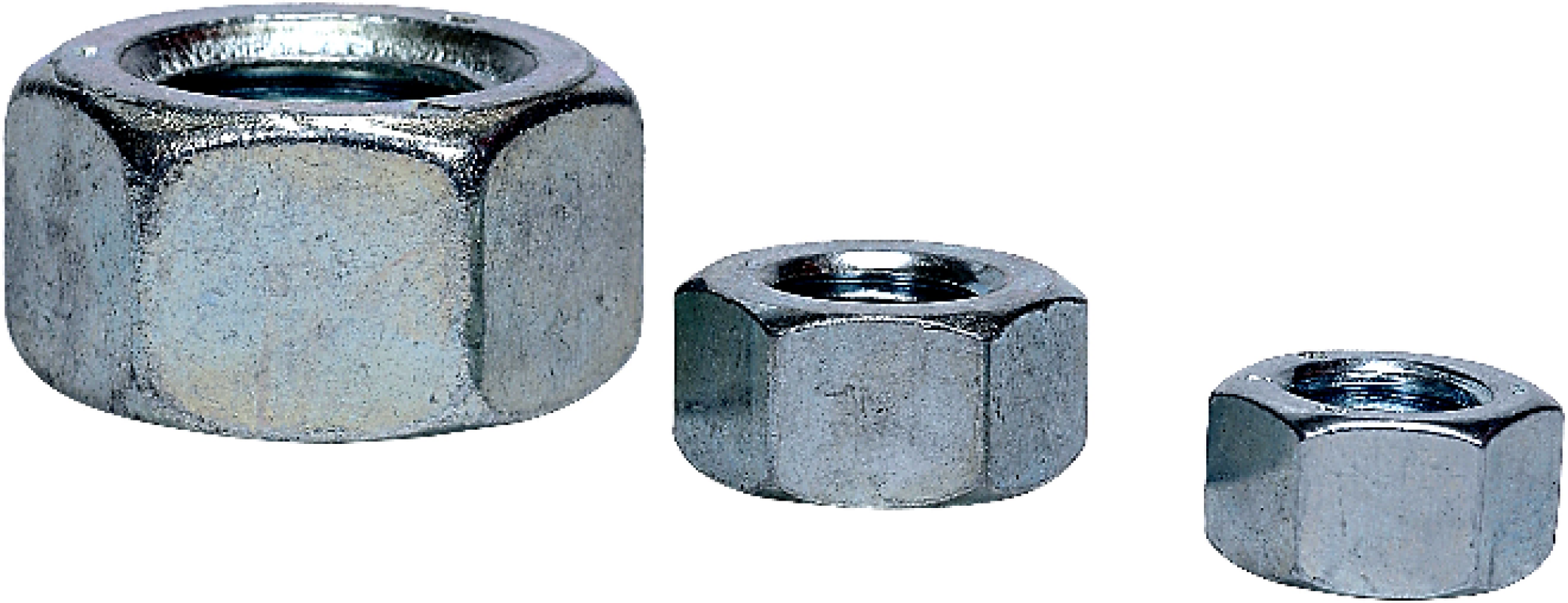

Original image for SLIC superpixel segmentation
Output Image
Superpixel segmentation using SLIC algorithm
The Code
import pathlib
from telekinesis import cornea
from datatypes import io
DATA_DIR = pathlib.Path("path/to/telekinesis-data")
# Load image
filepath = str(DATA_DIR / "images" / "nuts.jpg")
image = io.load_image(filepath=filepath)
# Perform SLIC superpixel segmentation
result = cornea.segment_image_using_slic_superpixel(
image=image,
num_segments=2,
compactness=15.0,
max_iterations=20,
enforce_connectivity=True,
)
# Access results
annotation = result["annotation"].to_dict()
mask = annotation['labeled_mask']The Explanation of the Code
SLIC superpixel segmentation clusters pixels in a 5D space (2D spatial + 3D color) to create compact, regular superpixels. It's one of the most popular superpixel algorithms.
The code begins by importing the required modules and loading an image:
import pathlib
from telekinesis import cornea
from datatypes import io
DATA_DIR = pathlib.Path("path/to/telekinesis-data")
filepath = str(DATA_DIR / "images" / "nuts.jpg")
image = io.load_image(filepath=filepath)The SLIC parameters are configured:
num_segmentscontrols the approximate number of superpixelscompactnessbalances color similarity vs. spatial proximitymax_iterationscontrols the number of clustering iterationsenforce_connectivityensures all superpixels are connected
result = cornea.segment_image_using_slic_superpixel(
image=image,
num_segments=2,
compactness=15.0,
max_iterations=20,
enforce_connectivity=True,
)The function returns a dictionary containing an annotation object in COCO panoptic format. Extract the mask as follows:
annotation = result["annotation"].to_dict()
mask = annotation['labeled_mask']Running the Example
Runnable examples are available in the Telekinesis examples repository. Follow the README in that repository to set up the environment. Once set up, you can run this specific example with:
cd telekinesis-examples
python examples/cornea_examples.py --example segment_image_using_slic_superpixelHow to Tune the Parameters
The segment_image_using_slic_superpixel Skill has many parameters. Key ones:
num_segments (default: 100):
- Approximate number of superpixels
- Units: Integer
- Increase for more, smaller superpixels
- Decrease for fewer, larger superpixels
- Typical range: 50-1000
compactness (default: 10.0):
- Compactness parameter balancing color vs. space
- Units: Dimensionless
- Increase for more compact, regular superpixels
- Decrease for more irregular, color-respecting superpixels
- Typical range: 1.0-40.0
max_iterations (default: 10):
- Maximum clustering iterations
- Units: Integer
- Increase for better convergence (slower)
- Decrease for faster processing
- Typical range: 5-20
enforce_connectivity (default: True):
- Whether to enforce superpixel connectivity
- Units: Boolean
- Set to
Truefor connected superpixels
TIP
Best practice: Start with default values. Adjust num_segments to control superpixel count, compactness to balance regularity vs. color respect.
Where to Use the Skill in a Pipeline
Segment Image Using SLIC Superpixel is commonly used in the following pipelines:
- Superpixel generation - Creating over-segmentation
- Object proposal generation - Generating candidate regions
- Image simplification - Reducing complexity
- Preprocessing - Initial over-segmentation for further processing
A typical pipeline for superpixel-based processing looks as follows:
from telekinesis import cornea
from datatypes import datatypes, io
# 1. Load the image
image = io.load_image(filepath=...)
# 2. Generate SLIC superpixels
result = cornea.segment_image_using_slic_superpixel(
image=image,
num_segments=200,
compactness=15.0,
)
# 3. Extract labels
annotation = result["annotation"].to_dict()
superpixel_labels = datatypes.Image(annotation['labeled_mask'])
# 4. Filter or process superpixels
filtered = cornea.filter_segments_by_area(
image=image,
labels=superpixel_labels,
min_area=10000,
)Related skills to build such a pipeline:
load_image: Load images from diskfilter_segments_by_area: Filter superpixels by areafilter_segments_by_color: Filter superpixels by colorsegment_image_using_felzenszwalb: Alternative superpixel method
Alternative Skills
| Skill | vs. Segment Image Using SLIC Superpixel |
|---|---|
| segment_image_using_felzenszwalb | Felzenszwalb produces irregular superpixels. Use SLIC for regular superpixels, Felzenszwalb for boundary-respecting regions. |
When Not to Use the Skill
Do not use Segment Image Using SLIC Superpixel when:
- You need irregular, boundary-respecting superpixels (Use Felzenszwalb instead)
- Speed is absolutely critical (Consider simpler methods)
TIP
SLIC is one of the most popular superpixel algorithms due to its balance of speed, regularity, and quality. It's widely used in computer vision pipelines.

