Segment Image Using GrabCut
SUMMARY
Segment Image Using GrabCut performs GrabCut segmentation.
GrabCut is an iterative segmentation algorithm that uses graph cuts to separate foreground from background. It can work with or without an initial bounding box, making it useful for interactive segmentation and object extraction.
Use this Skill when you want to segment foreground objects using iterative graph cut optimization.
The Skill
from telekinesis import cornea
result = cornea.segment_image_using_grab_cut(
image=image,
num_iterations=5,
bbox=None)Example
Input Image
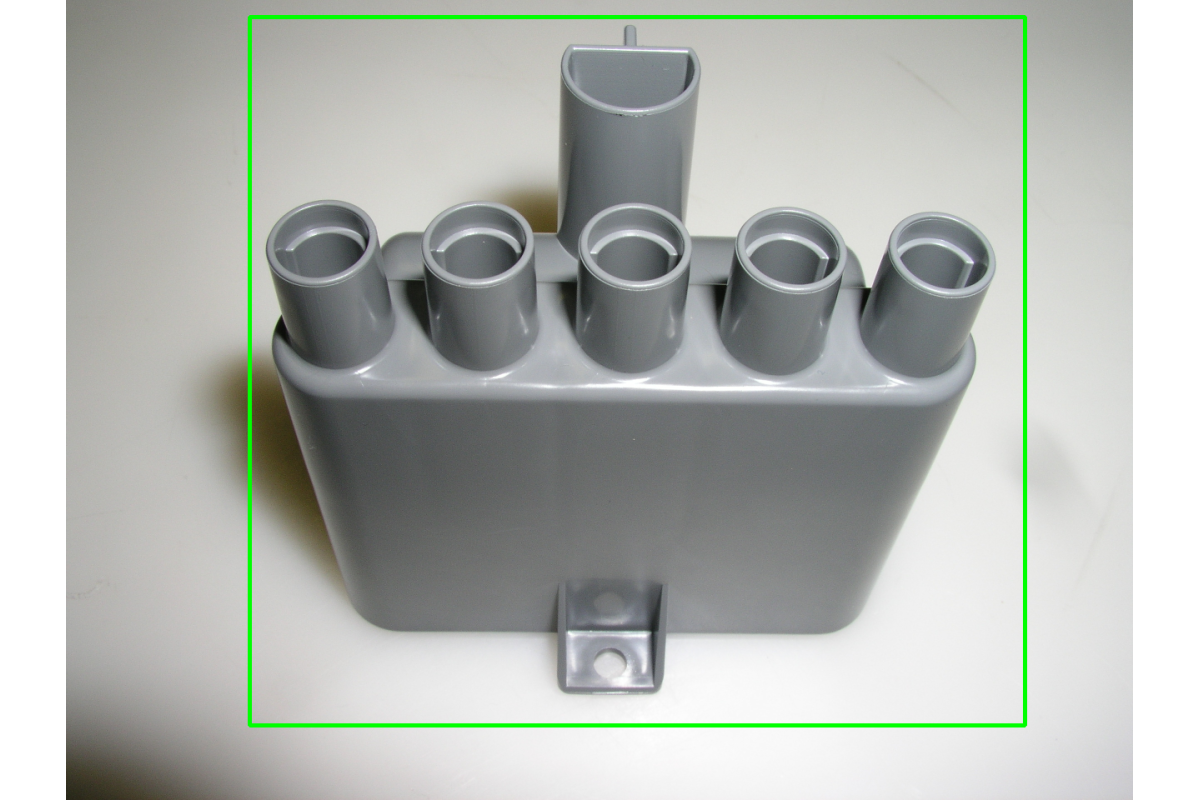

Original image for GrabCut segmentation
Output Image
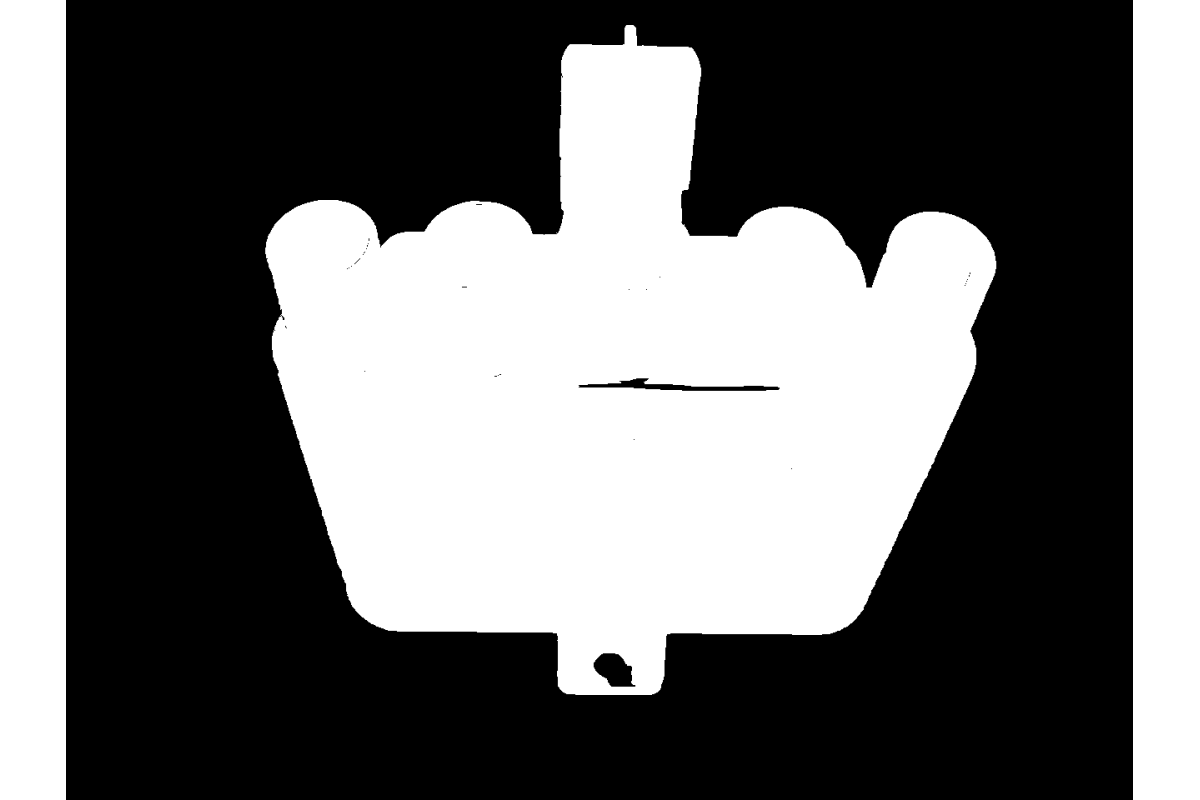
Foreground/background segmentation using GrabCut
The Code
import pathlib
import numpy as np
from telekinesis import cornea
from datatypes import io
DATA_DIR = pathlib.Path("path/to/telekinesis-data")
# Load image
filepath = str(DATA_DIR / "images" / "plastic_part.jpg")
image = io.load_image(filepath=filepath)
bbox = np.array([220, 20, 930, 850]) # [x, y, width, height] top left x and y
result = cornea.segment_image_using_grab_cut(
image=image,
num_iterations=2,
bbox=bbox,
)
# Access results
annotation = result["annotation"].to_dict()
mask = annotation['labeled_mask']The Explanation of the Code
GrabCut segmentation uses iterative graph cut optimization to separate foreground from background. It can work with an optional initial bounding box to guide the segmentation.
The code begins by importing the required modules and loading an image:
import pathlib
import numpy as np
from telekinesis import cornea
from datatypes import io
DATA_DIR = pathlib.Path("path/to/telekinesis-data")
filepath = str(DATA_DIR / "images" / "plastic_part.jpg")
image = io.load_image(filepath=filepath)The GrabCut parameters are configured:
num_iterations controls how many iterations the algorithm runs.
bbox is an optional bounding box (x, y, w, h) that can guide the segmentation.
result = cornea.segment_image_using_grab_cut(
image=image,
num_iterations=5, # Number of iterations
bbox=bbox,The function returns a dictionary containing segmentation results in COCO panoptic format.
Running the Example
Runnable examples are available in the Telekinesis examples repository. Follow the README in that repository to set up the environment. Once set up, you can run this specific example with:
cd telekinesis-examples
python examples/cornea_examples.py --example segment_image_using_grab_cutHow to Tune the Parameters
The segment_image_using_grab_cut Skill has 2 parameters:
num_iterations (default: 5):
- Number of iterations for GrabCut algorithm
- Units: Integer
- Increase for better results (slower)
- Decrease for faster processing
- Typical range: 3-10
bbox (default: None):
- Optional initial bounding box as
(x, y, w, h)tuple - Units: Pixel coordinates
- Provide to guide segmentation (faster, better results)
- None for automatic initialization
- Format: (top-left x, top-left y, width, height)
TIP
Best practice: Providing a bounding box around the object of interest significantly improves GrabCut results and reduces computation time.
Where to Use the Skill in a Pipeline
Segment Image Using GrabCut is commonly used in the following pipelines:
- Interactive segmentation - When user provides bounding box
- Object extraction - Extracting foreground objects
- Background removal - Separating objects from background
- Photo editing - Object isolation for compositing
A typical pipeline for interactive segmentation looks as follows:
from telekinesis import cornea
from datatypes import io
# 1. Load the image
image = io.load_image(filepath=...)
# 2. Get bounding box from user or detection
bbox = [x, y, w, h] # From user interaction or object detection
# 3. Apply GrabCut segmentation
result = cornea.segment_image_using_grab_cut(
image=image,
num_iterations=5,
bbox=bbox
)
# 4. Process segmented object
annotation = result["annotation"].to_dict()
mask = annotation['labeled_mask']Related skills to build such a pipeline:
load_image: Load images from disksegment_image_using_sam: Alternative interactive segmentation
Alternative Skills
| Skill | vs. Segment Image Using GrabCut |
|---|---|
| segment_image_using_sam | SAM is more modern. Use SAM for better results, GrabCut for traditional graph cut approach. |
| segment_image_using_flood_fill | Flood fill is simpler. Use flood fill for simple regions, GrabCut for complex objects. |
When Not to Use the Skill
Do not use Segment Image Using GrabCut when:
- You don't have a bounding box and need automatic segmentation (Use other methods)
- Speed is critical (GrabCut can be slower than simpler methods)
- Objects have very similar colors to background (May require more iterations or different method)
TIP
GrabCut is particularly effective for interactive applications where a user can draw a bounding box around the object of interest.

